What Are Smart Contracts? The 2025 Guide to AI-Powered Automation & Beyond
Published on: 28 Nov 2025
Here is a powerful, SEO-optimized blog post on "Smart Contracts", tailored to the 2025 landscape with a focus on real-world applications, AI integration, and security.
Metadata
- SEO Title: What Are Smart Contracts? The 2025 Guide to AI-Powered Automation & Beyond
- Meta Description: Discover the future of agreements with our ultimate guide to Smart Contracts in 2025. Learn how AI, cross-chain tech, and real-world asset tokenization are revolutionizing finance, supply chains, and more.
- Slug: /what-are-smart-contracts-2025-guide-ai-automation
- Focus Keyword: Smart Contracts
- Secondary Keywords: Blockchain automation, AI smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), real-world asset tokenization, cross-chain interoperability, smart contract security 2025, Ethereum, Solana.
- Tags: #SmartContracts, #Blockchain, #AI, #Web3, #Automation, #FinTech, #Crypto, #FutureOfWork
Smart Contracts: The Invisible Engine Powering the Global Economy in 2025
Imagine a world where you buy a house without a mountain of paperwork, get an insurance payout the second your flight is cancelled, or receive royalties instantly whenever your digital art is resold. No middlemen, no delays, no hidden fees.
In 2025, this isn't a futurist's dream. It's the reality being built on a foundation of smart contracts.
If blockchain is the digital ledger that records everything, smart contracts are the automated robots that do everything on that ledger. They are moving beyond simple crypto transactions to become the connective tissue of the modern digital economy.
Whether you're a developer, an investor, or a business leader, understanding smart contracts is no longer optional—it's essential. This guide will take you from the basics to the cutting-edge trends defining 2025.
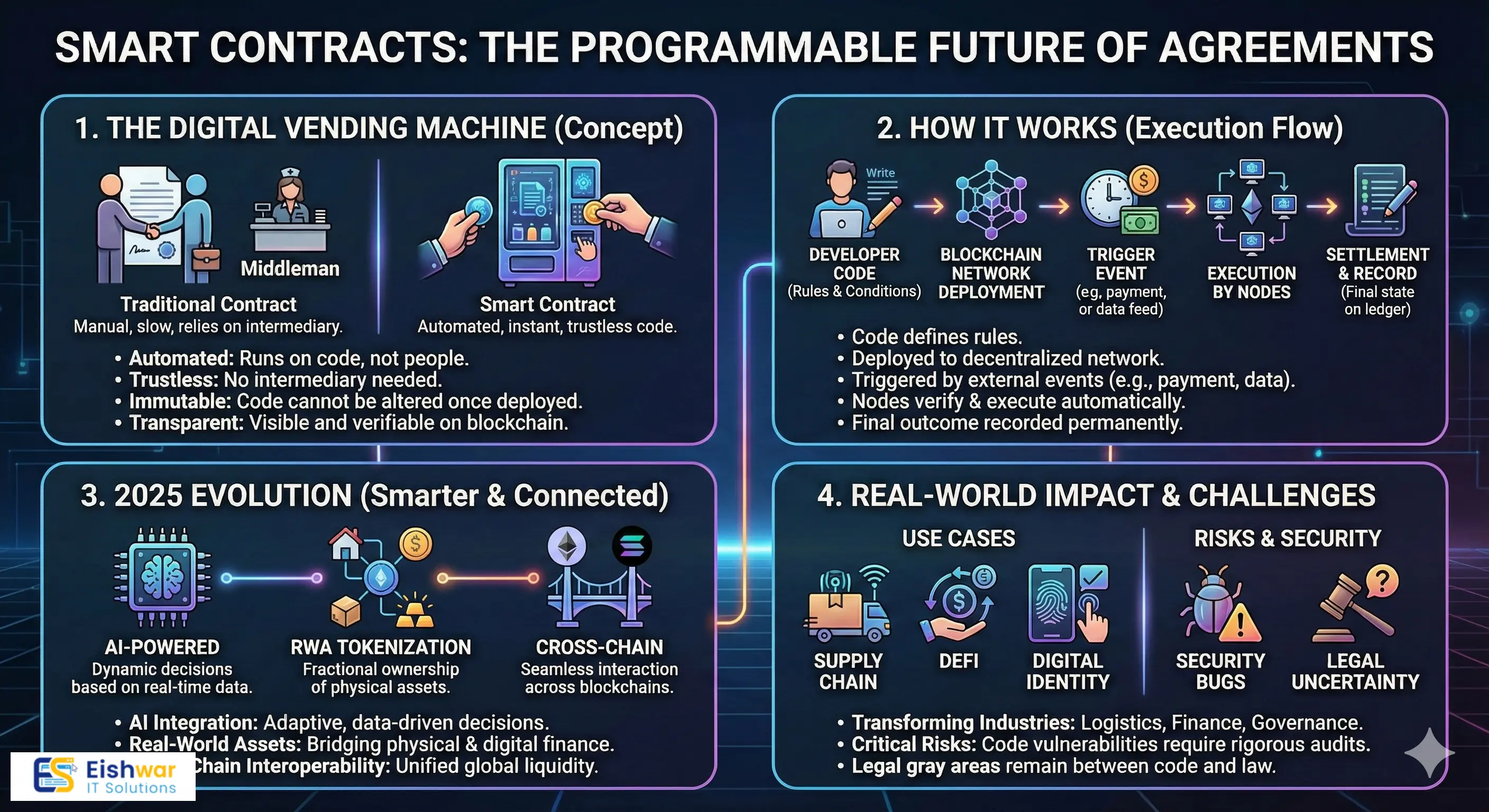
1. What is a Smart Contract? (The "If-This-Then-That" of Blockchain)
At its core, a smart contract is a self-executing computer program stored on a blockchain.
Think of it like a digital vending machine.
- Traditional Contract: You give money to a cashier (intermediary), who verifies it, then hands you a soda.
- Smart Contract: You put digital money into the machine. The machine's code automatically verifies the amount and instantly releases the soda. No cashier needed.
In technical terms, it's code that contains a set of rules and conditions agreed upon by parties. When these predefined conditions are met, the contract automatically executes the agreed-upon actions—like transferring funds, issuing a ticket, or registering ownership.
Key Characteristics:
- Automated: They run without human intervention once triggered.
- Trustless: You don't need to trust the other party or a middleman; you trust the code.
- Immutable: Once deployed on the blockchain, the code cannot be arbitrarily changed.
- Transparent: Anyone on the network can view the contract's logic and transaction history (on public blockchains).
2. How Smart Contracts Work: A Look Under the Hood
Smart contracts don't live in the cloud; they live on decentralized networks like Ethereum, Solana, or Polkadot. Here’s a simplified step-by-step process:
- Agreement & Coding: Two or more parties define the rules of their agreement (e.g., "If payment of 1 ETH is received, transfer ownership of digital artwork #123"). A developer writes this logic into code.
- Deployment: This code is compiled and deployed to a blockchain. It gets its own unique address, just like a user's wallet.
- Triggering Event: An external event occurs that interacts with the contract. This could be a user sending funds, an "Oracle" (a data feed) reporting a stock price, or another contract calling a function.
- Execution: Every node (computer) on the network runs the contract's code to verify the condition has been met.
- Settlement: Once consensus is reached, the action is executed (e.g., funds move, data updates) and recorded permanently on the blockchain.
Shutterstock
Explore
3. The Evolution: Smart Contracts in 2025
The smart contracts of today are far more powerful than the simple token-swapping scripts of 2017. In 2025, several key trends are redefining their potential.
A. The Rise of AI-Powered Smart Contracts
This is the biggest game-changer. Traditional smart contracts are rigid—they only do exactly what they are told. AI-powered smart contracts are dynamic and adaptive.
- How it works: By integrating with AI models (often via decentralized oracles), contracts can digest complex, real-world data to make decisions.
- Use Case: An insurance contract that doesn't just pay out on a "cancelled" flight status, but uses AI to analyze weather patterns, air traffic data, and news reports to predict delays and offer preemptive rebooking options or instant compensation.
B. Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization
Smart contracts are bridging the digital and physical worlds. We aren't just trading digital monkeys anymore; we're trading fractionalized ownership of real estate, government bonds, and commodities.
- The Role of the Contract: A smart contract manages the ownership stakes, automatically distributes rental income or dividends to token holders, and handles the instant transfer of these assets 24/7, bypassing traditional banking hours.
C. Cross-Chain Interoperability
In the past, a contract on Ethereum couldn't talk to a contract on Solana. Now, through advanced bridging protocols like LayerZero and Polkadot's XCMP, smart contracts can interact seamlessly across different blockchains. This creates a unified, global pool of liquidity and functionality.
4. Real-World Use Cases Transforming Industries
Smart contracts are stepping out of the crypto echo chamber and into the global economy.
Use Case 1: Supply Chain Management
- The Problem: Global supply chains are opaque, littered with paper trails and manual checks.
- The Smart Contract Solution: As a product moves from a factory to a shipping container to a warehouse, IoT sensors scan it. Each scan triggers a smart contract update on the blockchain, providing a real-time, tamper-proof history of the product's journey. Payments between suppliers and vendors can be automatically released as soon as a delivery is verified by the system.
Use Case 2: Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- The Problem: Traditional finance is slow, exclusive, and expensive.
- The Smart Contract Solution: DeFi is built entirely on smart contracts.
- Lending Protocols (e.g., Aave): A smart contract acts as the bank. You deposit collateral, and the contract automatically lets you borrow against it. Interest rates are set algorithmically based on supply and demand.
- Decentralized Exchanges (e.g., Uniswap): Smart contracts called "Automated Market Makers" (AMMs) allow users to trade tokens directly with a liquidity pool, with no central order book or middleman.
Use Case 3: Digital Identity & Voting
- The Problem: Online identity is fragmented and insecure; voting systems are vulnerable to fraud.
- The Smart Contract Solution: A user can hold a self-sovereign identity verified by a smart contract. For voting, a contract can issue one "vote token" to each verified identity. The user sends the token to their chosen candidate's address. The process is transparent, auditable, and prevents double-voting, all managed by code.
5. The Critical Challenges: Security and Law
Despite their power, smart contracts are not without huge risks.
Security Risks & Hacks
A smart contract is only as good as its code. If there is a bug, hackers will exploit it. Unlike a bank, there is no fraud department to reverse a transaction.
- The 2025 Solution: Security has become a massive industry. Before deployment, contracts now undergo rigorous multi-layered audits by specialized firms, combined with AI-driven scanning tools that look for common vulnerabilities like "reentrancy attacks."
The Legal Gray Area
Is a smart contract legally binding? The answer is still "it depends." While many jurisdictions are beginning to recognize them, there's a gap between code ("code is law") and legal systems that rely on human interpretation and intent. We are seeing the emergence of "hybrid" contracts that link on-chain code with off-chain legal agreements.
Conclusion: The Programmable Future
Smart contracts are the fundamental building blocks of a new, automated economy. They are shifting power from centralized institutions to open-source code, making processes faster, cheaper, and more transparent.
As AI continues to make these contracts smarter and they become deeply integrated with real-world assets, their impact will only grow. We are moving from a world of static paper agreements to a world of dynamic, programmable relationships.
The question isn't if smart contracts will affect your industry, but when. The best time to understand them is right now.
