The Definitive Guide to Blockchain Technology in 2025: Beyond the Hype
Published on: 27 Nov 2025
It is November 2025. The dust has long settled on the initial cryptocurrency frenzies of the early 2020s. What remains is something far more substantial, boring perhaps, but infinitely more revolutionary: the infrastructure of a new digital era.
For years, "blockchain technology" was a buzzword tossed around boardrooms and tech conferences, often misunderstood as synonymous only with volatile digital currencies. Today, we understand it for what it truly is: a foundational shift in how we manage data, establish trust, and transfer value in a digital-first world.
Blockchain has graduated from experimental pilots to production-grade reality. It is powering supply chains, securing identities, underwriting complex financial instruments, and forming the backbone of the emerging Web3 internet.
If you are still asking "What exactly is blockchain, and why does it matter now?" this guide is for you. We are moving beyond the jargon to provide a comprehensive, 2500-word deep dive into the mechanics, applications, and future of the technology that is redefining digital trust.
Chapter 1: De-mystifying the Jargon: What Actually is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is surprisingly simple. Forget the complex cryptography for a moment.
Imagine a standard spreadsheet, like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. This spreadsheet tracks transactions—Alice sent $20 to Bob; Charlie sent a digital document to Dave.
In the traditional world (Web 2.0), this spreadsheet lives on one central server owned by a bank, a tech company, or a government. They control it. If their server is hacked, the data is compromised. If they decide they don't like you, they can lock you out. You have to trust them completely.
Blockchain is that same spreadsheet, but with three radical changes:
1. It is Decentralized (Distributed Ledger Technology - DLT)
Instead of one master copy on one server, the exact same spreadsheet is duplicated across thousands of computers (called "nodes") all over the world. No single entity owns the network. To shut it down, you’d have to shut down every single computer simultaneously—a near impossibility.
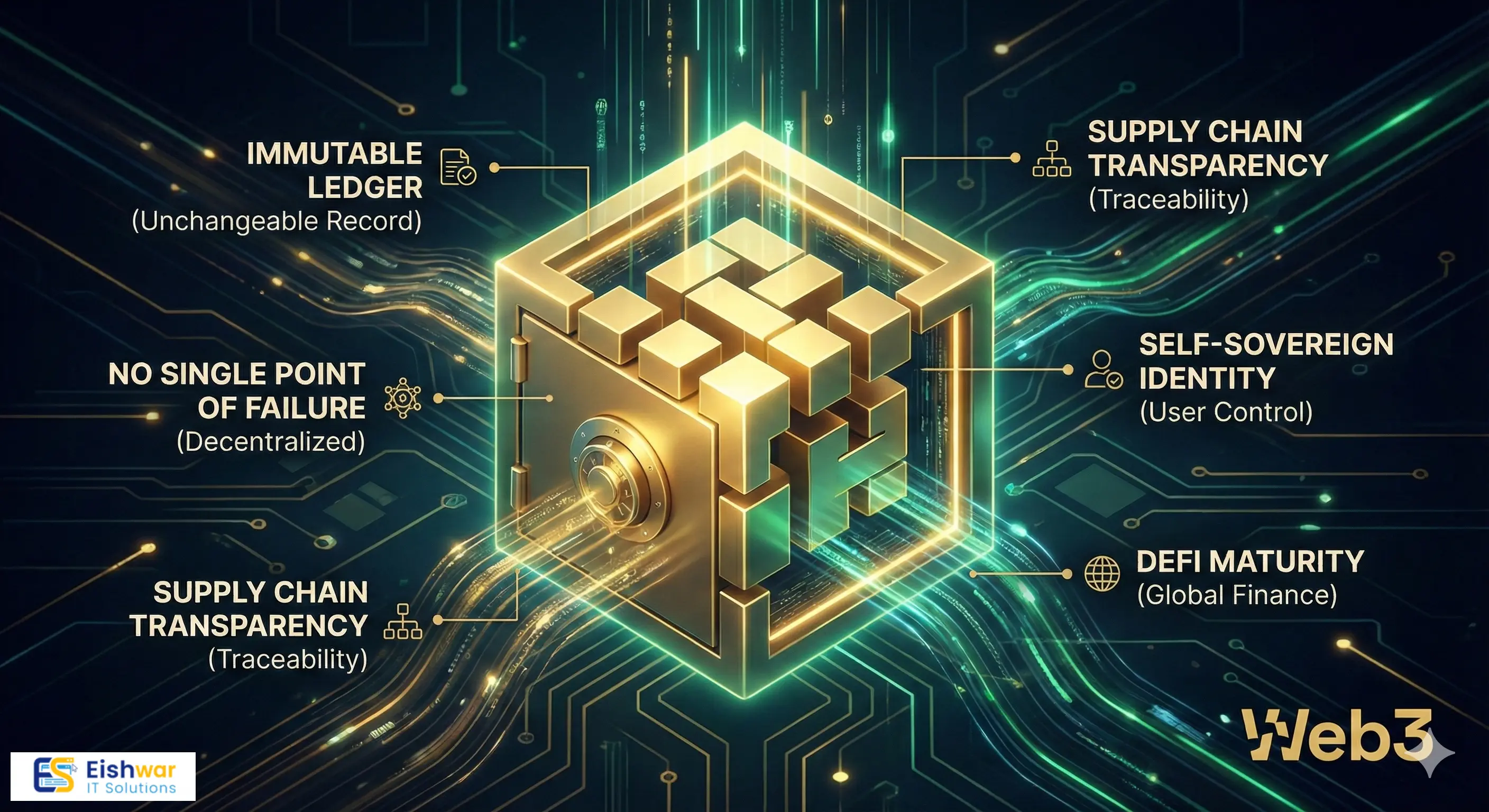
2. It is Immutable (Unchangeable)
This is the magic trick. Once a row is written into this spreadsheet, it cannot be deleted or edited. Ever. You can only add new rows that update the status of previous ones. This creates a perfect, audit-proof history of events that stretches back to the very first entry.
3. It is Transparent (Usually)
On public blockchains, anyone with an internet connection can view the spreadsheet in real-time. While the identities of the users are often pseudonymized by cryptographic addresses, the flow of value and data is visible to all. This radical transparency makes fraud incredibly difficult to hide.
In Summary: Blockchain is a shared, secure, and unchangeable record of information that doesn't require a central authority to manage it. It is a "trustless" system—meaning you don't need to trust the other person you are dealing with; you only need to trust the math powering the system.
Chapter 2: The Evolution: From Currency to World Computer
Blockchain didn't arrive in its current form overnight. Its evolution can be categorized into three distinct phases leading us to the mature landscape of 2025.
Blockchain 1.0: Digital Currency (The Bitcoin Era)
Starting around 2009 with Satoshi Nakamoto’s whitepaper, this phase was purely about money. Blockchain was employed as the underlying ledger for Bitcoin. Its sole purpose was to track who owned what amount of currency without needing a central bank. It proved that decentralized value transfer was possible and secure.
Blockchain 2.0: Programmable Finance (The Ethereum Revolution)
Around 2015, Ethereum changed the game. It realized that if a blockchain could track money, it could track anything. Ethereum introduced "Smart Contracts" (which we will detail in the next chapter). Suddenly, blockchain wasn't just a calculator; it was a global, decentralized computer. Developers could build applications on top of it.
Blockchain 3.0: The Web3 Infrastructure (The 2025 Landscape)
This is where we are today. Blockchain 3.0 is focused on solving the limitations of the previous eras—namely speed, cost, and environmental impact.
In 2025, we have moved past clunky, slow networks. We utilize highly scalable "Layer 2" solutions that sit on top of secure blockchains like Ethereum, making transactions instant and nearly free. We have achieved interoperability, meaning different blockchains can now "talk" to each other and exchange data seamlessly. Blockchain 3.0 is the invisible plumbing of the decentralized internet (Web3).
Chapter 3: The Engine Room: How It Works Under the Hood
You don't need to be a cryptographer to understand the basics of how the system maintains integrity.
The "Block" and the "Chain"
Imagine our spreadsheet again. When a group of new transactions occurs over a few seconds or minutes, they are bundled together into a "Block."
Before this block is added to the permanent record, it needs to be sealed. This seal is a unique digital fingerprint called a Hash. The genius is that the hash of the new block also contains the hash of the previous block.
This links them together chronologically in a literal "chain of blocks." If a hacker tries to go back five blocks and change an entry (e.g., give themselves more money), that block’s hash changes. Because the next block’s hash depended on the original one, that one breaks too. The entire chain forward becomes invalid. The network immediately spots the tampering and rejects the change.
The Consensus Mechanism: How We Agree
Since there is no central boss, how do thousands of nodes agree on which new block is legitimate? They use a "Consensus Mechanism."
- Proof of Work (PoW): The original mechanism used by Bitcoin. Computers race to solve complex mathematical problems to validate blocks. It is incredibly secure but energy-intensive.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): By 2025, this has become the dominant standard for smart contract platforms (Ethereum successfully transitioned years ago). Instead of energy-intensive mining, validators "stake" (lock up) their own capital as collateral to vouch for the honesty of transactions. If they act maliciously, they lose their stake. It is secure, fast, and environmentally friendly.
The Killer App: Smart Contracts
This is the most critical concept for modern business applications.
A smart contract is simply code written onto the blockchain that executes automatically when certain conditions are met. It is "If This, Then That" logic that no one controls once deployed.
- Traditional Example: You buy a house. You send money to an escrow lawyer. The lawyer waits for the deed. Once both are present, the lawyer swaps them. You pay the lawyer a large fee.
- Smart Contract Example: You send digital currency to a smart contract address. The seller sends the digital deed token to the same contract. The code detects both assets are present and automatically swaps them instantly. No lawyer, no fee, no delay.
Chapter 4: Real-World Applications in 2025
In 2025, we are no longer talking about theoretical pilots. Blockchain technology is actively reshaping major global industries.
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Maturity
DeFi has matured from a "wild west" into a serious alternative financial infrastructure. Today, billions of dollars in lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance happen directly between users via smart contracts, bypassing traditional banks. We now see "Real World Assets" (RWAs)—like real estate deeds or corporate bonds—being tokenized and traded on DeFi platforms 24/7 with instant settlement.
2. Supply Chain Provenance
This is one of the most successful implementations. Consumers in 2025 demand to know the ethical and safety history of their products.
Blockchain provides an unbroken chain of custody. A coffee bean can be tracked from the farmer in Colombia to the roaster in Seattle to the cafe in London. Every step—harvesting, shipping, customs clearance, roasting—is an immutable entry on the blockchain. Walmart, Maersk, and luxury brands utilize this to fight counterfeiting and ensure quality control instantly.
3. Digital Identity (Self-Sovereign Identity - SSI)
The era of logging into 50 different websites with the same email and password is ending. Blockchain enables Self-Sovereign Identity.
You hold your verified credentials (driver's license, university degree, proof of age) in your secure digital wallet. When a website needs to know if you are over 21, you don't upload a photo of your ID to their insecure server. Your wallet simply provides a cryptographic "proof" that you are over 21 without revealing your birthdate or name. You own your identity data, sharing only what is necessary.
4. Healthcare Data Silos
Patient data has historically been trapped in silos across different hospitals. Blockchain is being used to create a unified, patient-controlled electronic health record. Doctors can request access to your complete history, and you grant permission via your private key. This improves diagnoses and ensures data integrity across different providers.
5. Intellectual Property and NFTs (Beyond JPEGs)
While the cartoon ape craze of 2021 seems quaint now, the underlying technology of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) is vital. An NFT is simply a blockchain-based deed of ownership for a unique digital or physical asset.
In 2025, musicians use NFTs to receive royalties instantly every time their song plays. Digital artists retain provenance of their work. Even physical house deeds are increasingly being registered as NFTs on government-sanctioned blockchains to prevent title fraud.
Chapter 5: The Elephants in the Room: Challenges Remaining
Despite massive progress, blockchain technology in 2025 is not a magic bullet for every problem. Significant hurdles remain that developers and regulators are actively addressing.
The "Blockchain Trilemma"
This is the classic engineering trade-off. It is incredibly difficult to achieve Decentralization, Security, and Scalability all at the same time. Usually, you only get two.
If you want high speed (Scalability), you often have to centralize the network slightly (sacrificing Decentralization). The industry has mostly solved this through "Layer 2" networks that handle speed off the main chain, but it remains a complex balancing act.
The Regulatory Landscape
By 2025, regulations have become clearer, but the global patchwork is complicated. Governments are grappling with how to tax DeFi, how to apply securities laws to tokens, and how to manage decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) that have no physical headquarters. Furthermore, the rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)—government-issued crypto—is creating friction with the decentralized ethos of public blockchains.
User Experience (UX) Friction
While vastly improved since the early days, interacting with blockchain applications is still too complex for your average grandmother. Managing private keys, understanding "gas fees," and bridging assets between chains is a friction point that Web3 interface designers are desperately trying to abstract away so it feels like using a normal Web2 app.
Chapter 6: The Future Outlook: The Invisible Fabric
As we look toward 2030, the goal of blockchain technology is to become invisible.
When you send an email today, you don't think about the TCP/IP protocols that make it possible; you just hit send. The future of blockchain is similar. It will just be the underlying "operating system of trust" that powers the internet.
We are seeing the early stages of the convergence of Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain. AI agents will likely become the primary users of blockchain networks, using smart contracts to autonomously negotiate resources and execute complex tasks in the machine-to-machine economy.
We are moving toward a world where "don't be evil" (the motto of centralized Web2 tech giants) is replaced by "can't be evil." A world where integrity is guaranteed not by promises, but by cryptographic proof.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has proven its resilience. It survived bear markets, skepticism, and regulatory crackdowns to emerge as a fundamental pillar of the 2025 digital economy.
Whether you are a business leader looking to optimize efficiency, a developer looking to build the next generation of applications, or simply a citizen concerned about data privacy, understanding blockchain is no longer optional—it is essential literacy for the modern world. The revolution is no longer coming; it is running in the background right now.
