Web3: The Next Evolution of the Internet and the Future of Digital Freedom
Published on: 28 Nov 2025
Introduction: The dawn of a New Digital Era
Imagine an internet where you don't just browse, scroll, and click, but you actually own your digital footprint. Imagine a world where your data isn't harvested by advertising giants to be sold to the highest bidder, but instead remains locked in a digital vault that only you hold the key to. Imagine a financial system that operates 24/7 without a single bank manager, or a social network where no central authority can ever silence your voice.
This is not science fiction. This is the promise of Web3.
The internet is currently undergoing its most significant transformation since its inception. We are transitioning from the era of "Big Tech" dominance to an era of user sovereignty. Web3 is more than just a technological upgrade; it is a philosophical movement that seeks to democratize the web, redistribute power from the few to the many, and rewrite the fundamental rules of how we interact, transact, and exist online.
For businesses, developers, investors, and everyday users, understanding Web3 is no longer optional—it is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will peel back the layers of this complex ecosystem to reveal how Web3 is building the future of digital freedom.
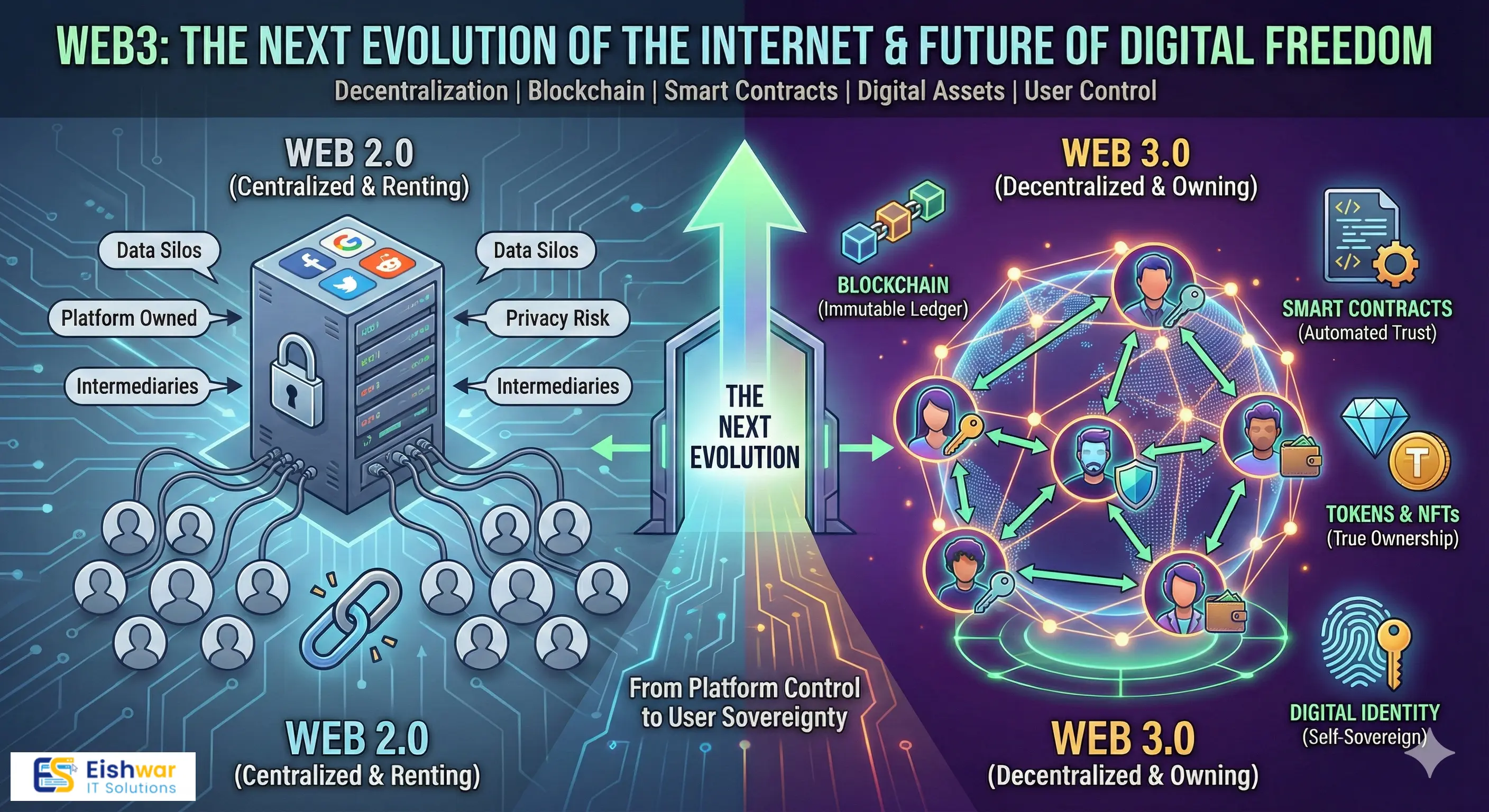
1. The Evolution of the Web: How Did We Get Here?
To truly grasp the magnitude of Web3, we must first look at the history of the internet through the lens of evolution. The web has grown in distinct stages, each defined by how users interact with data.
Web 1.0: The "Read-Only" Web (1990–2005)
In the beginning, the internet was a library. It was static, disorganized, and simple. Web 1.0 was characterized by decentralized protocols where most users were passive consumers of content. You could go to a website and read a news article or look at a company’s homepage, but there was almost no interaction. Creating content required technical coding skills, meaning the flow of information was strictly one-way: from the publisher to the reader. It was an open frontier, but a quiet one.
Web 2.0: The "Read-Write" Web (2005–Present)
Then came the social revolution. Web 2.0 introduced interactivity, social media, and user-generated content. Suddenly, anyone could be a creator. We gained the ability to post videos on YouTube, share thoughts on Twitter, and connect with friends on Facebook.
However, this convenience came at a hidden cost. To make these platforms work, we centralized the internet. We flocked to "walled gardens"—closed ecosystems run by massive corporations like Google, Meta (Facebook), Amazon, and Apple. In exchange for free services, we surrendered our data. These companies became the gatekeepers, monetizing our attention and creating an internet where users are the product, not the owners. This model created a "feudal" internet where a few kings rule over billions of digital serfs.
Web 3.0: The "Read-Write-Own" Web (The Future)
Web3 is the reaction to the centralization of Web 2.0. It is the "Read-Write-Own" phase of the internet. By leveraging blockchain technology and cryptography, Web3 allows users to participate in the creation of the web while retaining ownership of their contributions.
In Web3, you don’t have a profile that belongs to Facebook; you have a digital identity that belongs to you. You don’t earn loyalty points that can be revoked by an airline; you earn tokens that have real-world value and can be traded. It breaks down the walled gardens and restores the open, decentralized vision of the early internet—but with the modern functionality we’ve grown to love.
2. How Web3 Works: The Architecture of Trust
Web3 is not a single piece of software; it is a stack of technologies working in harmony to remove intermediaries. It replaces the "trust" we place in humans (bankers, lawyers, tech CEOs) with trust in code and mathematics.
The Backbone: Blockchain Technology
At the heart of Web3 lies the blockchain. A blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that records transactions and data across a network of computers (nodes) rather than on a central server. Because the data is distributed across thousands of computers, it cannot be unilaterally altered, deleted, or hacked by a single entity. This creates a "trustless" environment—you don't need to trust the other person to transact with them; you only need to trust the system, which is transparent and verifiable by anyone.
The Logic: Smart Contracts
If the blockchain is the database, Smart Contracts are the operating system. These are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met.
Think of a smart contract like a digital vending machine. In a traditional deal (like buying a house), you need lawyers and escrow agents to ensure the money is paid and the title is transferred. This takes weeks and costs thousands. With a smart contract, the code says: "If User A sends the funds, transfer the digital title to User A immediately." It happens instantly, without a middleman, and the code is law. This automation is what allows Web3 applications to run autonomously.
The Keys: Crypto Wallets and Digital Identity
In Web 2.0, you have a different username and password for every site. In Web3, you have a Wallet (like MetaMask or Phantom). This wallet is your universal passport. You use it to log in to websites, store your money, hold your digital art, and cast votes in online communities. Because you hold the "Private Keys" to this wallet, no government or corporation can freeze your account or deny you access. You are the sovereign ruler of your digital existence.
3. The Pillars of the Web3 Philosophy
Why are people so passionate about Web3? It isn't just about cool tech; it's about solving fundamental societal problems.
True Digital Ownership
In a video game like Fortnite, you might buy a "skin" for your character. But do you own it? No. If the game developers delete your account, that money is gone. In Web3, digital assets are issued as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). If you buy a sword in a Web3 game, that sword lives in your wallet, not the game's server. You can take it out of the game, sell it on a marketplace, or even potentially move it to a different game. This concept extends to art, music, data, and even real estate.
Censorship Resistance
Because Web3 runs on decentralized networks, there is no "off switch." A government cannot pressure a central server to remove a piece of content because the content exists on thousands of nodes simultaneously. This makes Web3 a vital tool for free speech and information preservation in an era of increasing digital surveillance and control.
The Token Economy
Web3 aligns incentives through Tokenomics. In Web 2.0, the value created by users (content, data, interactions) is captured by the platform. In Web3, users are rewarded with tokens for their participation. If you help govern a community, provide liquidity to a market, or create popular content, you earn a stake in the network itself. This shifts the model from "extraction" to "community ownership."
4. Core Components and Real-World Applications
Web3 is already changing the world through several key verticals.
DeFi: Decentralized Finance
DeFi is perhaps the most mature sector of Web3. It is an open financial system that operates without banks. Through DeFi protocols like Uniswap or Aave, users can lend money to earn interest, borrow funds against their assets, and trade currencies 24/7. It democratizes access to financial services, allowing anyone with an internet connection—regardless of their credit score or nationality—to participate in the global economy.
DAOs: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
A DAO is a business that runs on code, not management. Instead of a CEO and a Board of Directors, a DAO is governed by its community of token holders. Decisions regarding the organization’s treasury, roadmap, and rules are made via transparent voting on the blockchain. This represents a radical shift in corporate governance, enabling global collaboration without bureaucracy.
The Metaverse and Spatial Computing
While the Metaverse is often confused with Web3, they are distinct yet connected. Web3 provides the economic layer for the Metaverse. If we are going to spend time in virtual worlds, we need a way to prove we own our avatars, our virtual land, and our digital clothes. Web3 ensures that the Metaverse remains an open economy rather than a theme park controlled by a single corporation like Meta.
Supply Chain and Traceability
Beyond finance, Web3 is revolutionizing logistics. By using blockchain, companies can create an immutable history of a product’s journey. A consumer buying coffee can scan a QR code and see exactly which farmer grew the beans, when they were harvested, and how much the farmer was paid, ensuring ethical sourcing and authenticity.
5. The Challenges: The Roadblocks Ahead
Despite its promise, Web3 is not without its flaws. We must be realistic about the hurdles that need to be overcome before mass adoption can occur.
Scalability and Speed
Current blockchains are often slower and more expensive than centralized servers. When thousands of people try to use Ethereum at once, transaction fees ("gas fees") can skyrocket. For Web3 to compete with Visa or Twitter, it needs to process millions of transactions per second at near-zero cost. Layer-2 solutions (like Polygon and Arbitrum) are currently solving this, but we are not fully there yet.
User Experience (UX)
Right now, Web3 is difficult to use. Managing private keys, understanding "gas," and navigating complex interfaces is a nightmare for the average person. One mistake—like sending money to the wrong address—can result in a total loss of funds. For Web3 to succeed, the technology needs to become invisible. Users shouldn't need to know they are using a blockchain; it should just work.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments around the world are scrambling to figure out how to regulate this new space. Is a token a security? How do you tax a DAO? While regulation is necessary to prevent fraud and protect consumers, overly aggressive laws could stifle innovation and drive development underground.
Environmental Concerns
Early blockchains like Bitcoin use "Proof of Work," which consumes vast amounts of energy. However, the industry is rapidly shifting toward "Proof of Stake" mechanisms (like the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade), which reduce energy consumption by over 99%, effectively neutralizing this criticism for the new generation of Web3 technology.
6. The Future: Where Do We Go From Here?
We are currently in the "dial-up" phase of Web3. The infrastructure is being built, the pioneers are testing the waters, and the rules are being written in real-time.
As we look to the future, we can expect Web3 to become the invisible backend of the internet. We will likely see the rise of "Hybrid Web3," where traditional companies integrate blockchain features—like Starbucks using NFTs for loyalty programs or Ticketmaster using smart contracts to prevent scalping.
We will see the rise of Self-Sovereign Identity, where you can verify your age, credentials, and medical history without revealing sensitive personal data, drastically reducing identity theft.
Ultimately, Web3 represents a pendulum swing back toward the original vision of the internet: a collaborative, open space for humanity. It empowers the creator over the platform, the individual over the institution, and the code over the corruptible human intermediary.
Conclusion
Web3 is not just a technological upgrade; it is a movement for digital freedom. It challenges the status quo of the current internet, asking us to reimagine how we value data, how we trust one another, and how we define ownership in a digital age.
While the road ahead is filled with technical challenges and regulatory battles, the destination is worth the struggle. We are building a web that is more resilient, more fair, and more human-centric. The transition from Web2 to Web3 is inevitable because the demand for ownership and privacy is universal.
The future of the internet is not about being a user; it’s about being an owner. Welcome to Web3.
